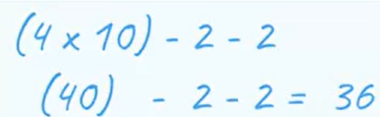Codeblocks - use Math blocks
Use Math blocks to add, subtract, multiply, divide, and round numbers, as well as to find the square root and perform trigonometry functions.
Step-by-step guide
Math code blocks contain mathematical blocks to perform a variety of operations. These include a Number constant block, a block with Operations of arithmetic, a block with Square Root and other common functions, a Trigonometry block, a Rounding block, a Remainder Of block, and a Constrain block to limit a number between a minimum and a maximum value.
When working with mathematical code blocks, it is important to understand the relationship between block grouping and the order of operations.
An arrangement of blocks is created with an intended result of 36, as shown in the calculation.
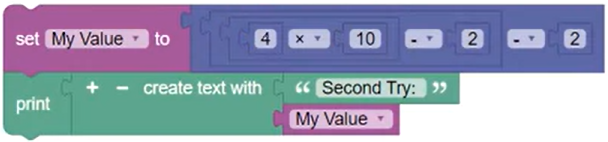
However, each block in the following block set acts as a grouped parenthetical calculation. When the code block is run, the result of the following configuration is 40.
The same blocks are rearranged and grouped to achieve the expected result of 36.
To set up a rule that calculates the area of a wall, first, add the Area parameter to the form:
- In Inventor, add a parameter for Area to hold the calculated square footage.
- In the Parameters tab of the Product definition, select Area to add it to the form.
- Click the Rules tab to view the added Area parameter.
The product definition shown below has already been set up to display the length and height in form messages as inches.
- If needed, to view the contents of a collapsed block, right-click and select Expand Block.
- To collapse it again, right-click and select Collapse Block.
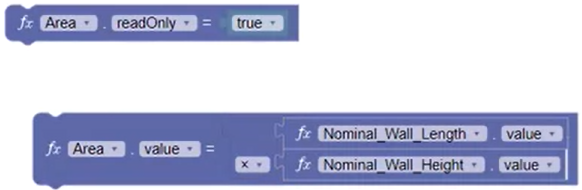
To make the Area parameter read-only:
- Add a Nominal Wall Length parameter block. Set the parameter to Area and the function to readOnly.
- Finish the statement by adding a True False block with a value of true.
To create the Area calculation:
- Create another Area block.
- Add another Length block, then copy and paste it using CTRL+C and CTRL+V. Change the second parameter to Nominal Wall Length.
- Add an Operations math block to the Area block, set the operation to Multiply, and add the Length and Height parameter blocks to create the Area calculation.
- Right-click the Area block and select External Inputs to wrap the block.
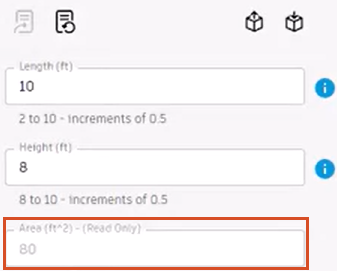
- Click Update form.
The Area calculation displays in the form as a read-only value.
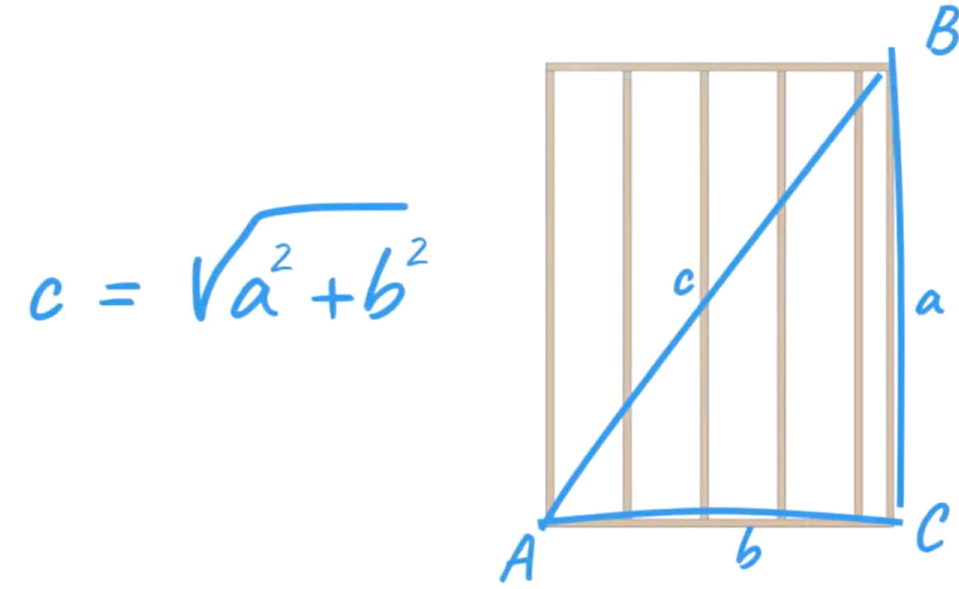
Next, to determine the diagonal measurement of the wall from corner to corner, transform the Pythagorean theorem to solve for length c.
- Add a Set to variable block and set it to Diagonal. Add and connect a Square Root Math block to the Diagonal block.
- Add two Operations Math blocks. Leave the first set to addition (+), and change the second to exponentiation (^), to raise the value by a power of 2.
- Add a Nominal Wall Length parameter to the Squared block. Duplicate this block to create the same block for the Height parameter.
- Add the Squared blocks to either side of the Addition block to sum the results of both squared parameter values.
- Right-click and select External Inputs to wrap the blocks to fit better in the canvas.
- Add the Squared blocks to the Diagonal Square Root block.
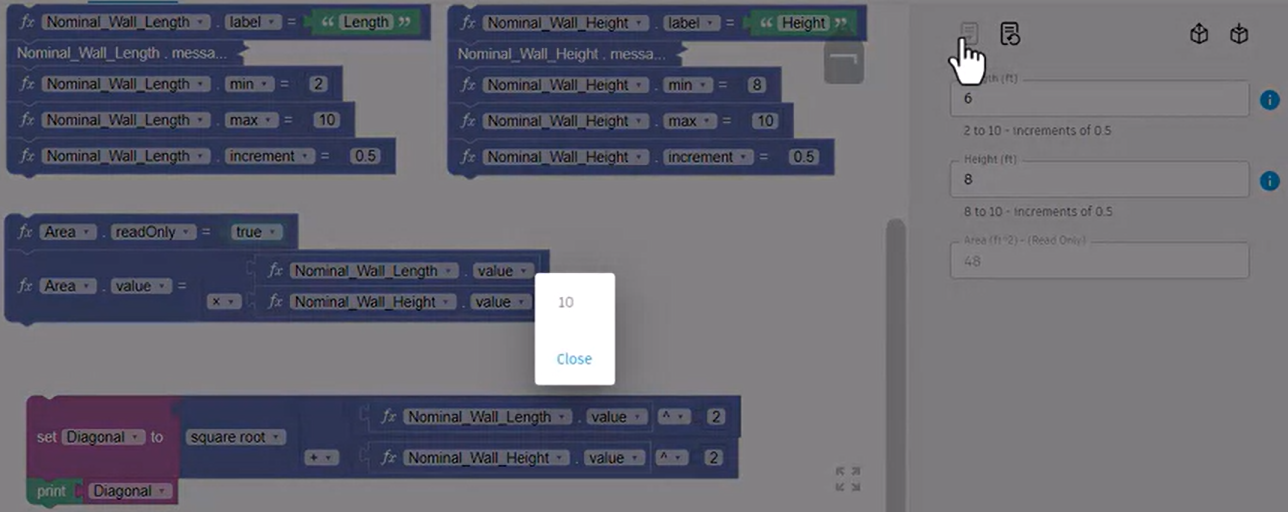
- To set the Diagonal result to print when the form is updated, below the Diagonal Square Root block, add a Print block and attach a Diagonal variable block.
- Click Update form.
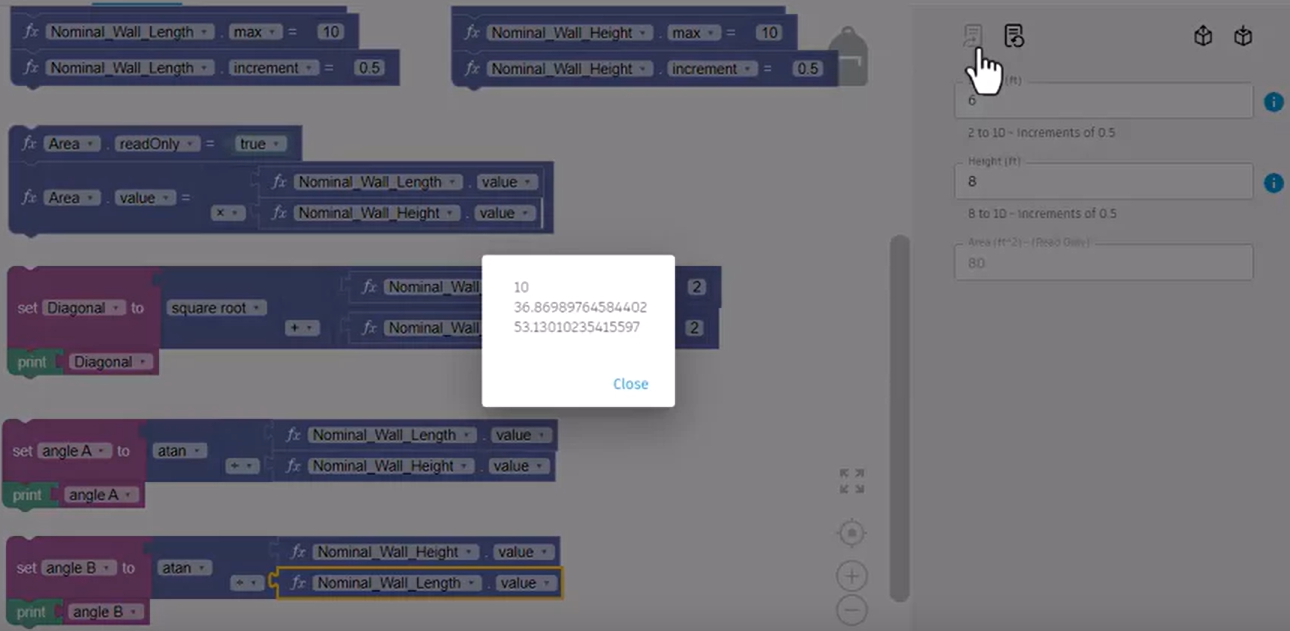
A popup shows the Diagonal result.
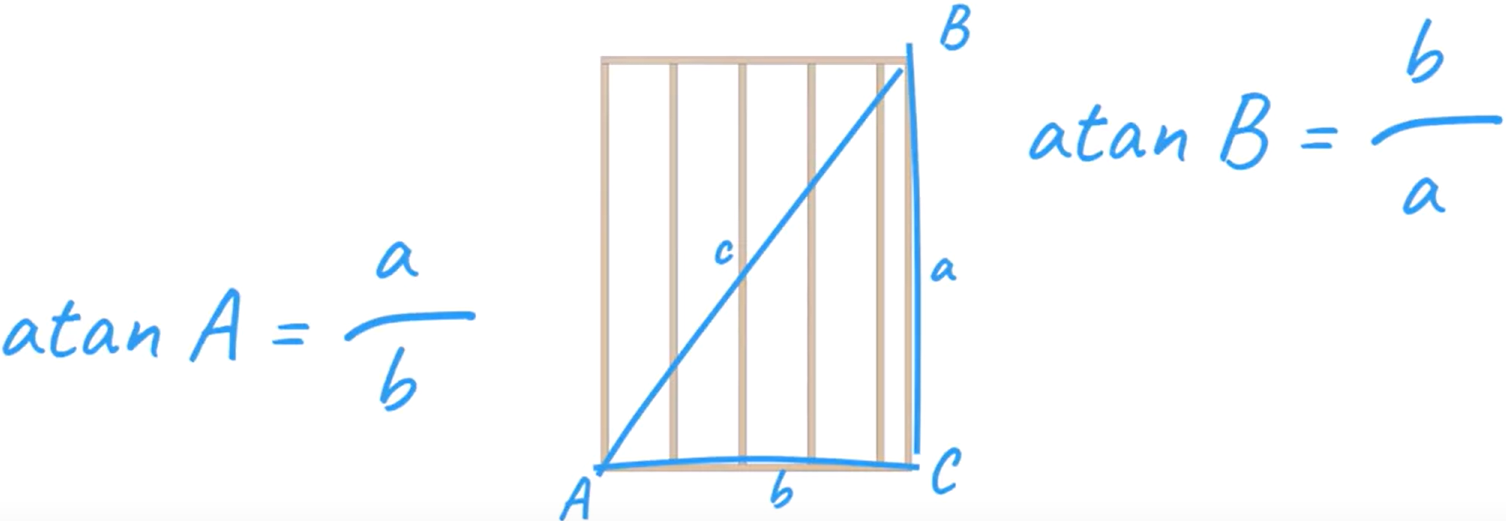
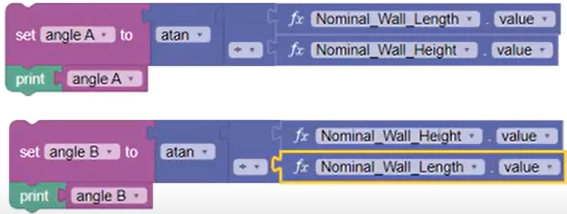
The angles of the diagonal corners can be calculated using the Inverse Tangent Trigonometric block.
- Right-click the Diagonal Square Root block set and select Duplicate Connected. Remove the Square Root portion of the equation.
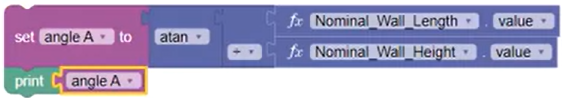
- Add a Trigonometry math block and set the function to atan.
- From the Area calculation, Duplicate the Length multiplied by Height block, add it to the Atan block, and change the Operation to Division.
- Change the Set To and Print variable blocks to a previously created variable, angle A.
- Right-click and select Duplicate Connected to copy the entire block. Set the drop-down to angle B, and then swap the Height and Length parameters.
- Click Update form.
The result for the Diagonal, along with the result for Angle A and Angle B display in the popup.
In summary, Math blocks evaluate as parenthetical groups following the standard order of operations. There are numerous Math blocks that can be combined to perform a variety of mathematical calculations.